

Partition Scheduling
In safety-critical applications, a major concern is that critical tasks are never starved for CPU time. Tasks dedicated to safety must always have the opportunity to run. However, the scheduler in a real-time system generally uses a priority scheme for deciding between threads contending for CPU time and does not account for the amount of CPU time allotted. The sole criteria is thread priority.
QUARC's QNX target provides an elegant solution to this dilemma - partition scheduling. There are two major varieties of partition scheduling on the market: fixed partition scheduling and adaptive partition scheduling. Partition scheduling is currently only available on the QUARC QNX target.
Fixed Partition Scheduling
In fixed partition scheduling paradigms, based on standards such as ARINC 653, a process or thread may be assigned to a particular scheduler partition. Each partition is assigned a fixed bound on its CPU time. For example, partition A may be allotted 20% of the CPU time and partition B 80% of the CPU time. Threads in partition A are restricted to 20% of the CPU time, even if they attempt to use all available CPU time. Likewise, if threads in partition B only use 50% of the overall CPU time then the remaining 30% allotted to partition B is never used. CPU time is wasted, but critical tasks do get the CPU time required. Partitions may only be configurable at boot time or when a boot image is created.
Adaptive Partition Scheduling
The QNX Neutrino real-time operating system may be configured to use a partition scheduler (see the aps command). Unlike a fixed
partitioning scheme however, QNX provides an adaptive partition scheduler. In adaptive partition scheduling, processes
or threads are still assigned to particular partitions, but the CPU-time bounds on those partitions
are dynamic. The CPU time bounds assigned to each partition are always guaranteed, but the system
distributes a partition's unused resources among partitions that require additional resources when
the system isn't loaded. Thus, use of computing resources is maximized without compromising the
minimum latencies of critical tasks.
Partitions may be added and configured at run-time. Each partition is assigned a set of rules that govern its use of system resources. When a process or thread becomes a member of a partition, it is then constrained by the rules governing that partition.
| On x86 systems, turn off any BIOS configuration that may cause the system to enter System Management Mode (SMM), such as USB legacy support, for proper operation of adaptive partitioning. |
QUARC supports adaptive partitioning via the model arguments. This simple mechanism allows a model to be assigned to a specific adaptive partition, either by name or identifier. The partition must be created before running the model. Assigning a model to a partition does not cause the partition to be created - the model simply joins a pre-existing partition.
To configure a model to run in a particular partition, simply add the -part <name or ID> option anywhere
the model arguments may be specified.
Assigning the Partition from Simulink
For example, to set the partition from Simulink, add the -part <name or ID> option to the model arguments
in the MEX-file arguments field of the
Code Generation/QUARC
tab of the Configuration Parameters dialog. Typical MEX-file
arguments in this case would be:
'-w -d %d -uri %u -part partitionA'
where the -part option assigns the model to an adaptive partition called "partitionA". This partition must
already have been created using the aps command on the QNX target. The partition can also be specifed by
its numeric identifier. For instance:
'-w -d %d -uri %u -part 1'
would assign the model to partition 1.
Assigning the Partition Using the quarc_run Command
The partition associated with a model may also be set when invoking the model via the quarc_run command.
To load a model via quarc_run the -l option is used. For example, running the following command
on the QNX target:
quarc_run -l my_model.rt-qnx_x86 -part partitionA
loads a QUARC model called "my_model.rt-qnx_x86" that has already been downloaded to the QNX target. The model will be assigned to an adaptive partition called "partitionA".
|
Note that the |
Assigning the Partition Using Windows Explorer
The adaptive partition assigned to the QUARC model may also be configured when invoking the model from Windows Explorer. Right-click on the model executable to bring up the context menu. Select the item to open the dialog shown below:
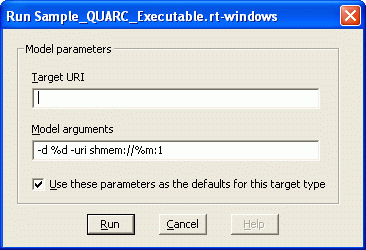
In the Model arguments field add the -part <name or ID> option to the list of arguments.
For instance:
-d %d -uri tcpip://qnx-dev:17001 -part partitionA
would assign the model to an adaptive partition called "partitionA". If the Use these parameters as the defaults for this target type option is checked then these arguments will be used as the defaults. In that case, simply double-clicking on the model executable will run the model on the target and assign it to the specified partition.
Refer to Using Windows Explorer to Manage Models for more information on using Windows Explorer to run models on any local or remote target, including QNX.
Assigning the Partition Using A Supervisory Model
QUARC's dynamic reconfiguration facilities allow a model to take upon a supervisory role, managing other models. Models can be downloaded and run using Simulink blocks. When loading a model via the dynamic reconfiguration blockset, the model arguments may also be specified. Thus, the supervisory model can also assign models to specific adaptive partitions!
The two dynamic reconfiguration blocks which allow models to be loaded are the Target Load Model block and the Target Switch Model block. To assign a model to "partitionA", add the "-part partitionA" option to the Arguments for model to load parameter of the Target Load Model block. When the block is executed, it will load the model and assign it to the adaptive partition called "partitionA". The procedure is similar for the Target Switch Model block. Simply add the "-part partitionA" option to its Arguments for model to switch in parameter.

Copyright ©2025 Quanser Inc. This page was generated 2025-11-01. Submit feedback to Quanser about this page.
Link to this page.