

Synchronize
Synchronizes two signals.
Library
QUARC Targets/Discontinuities MATLAB Command Line Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window: qc_open_library('quarc_library/Discontinuities')
Description
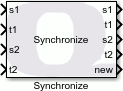
The Synchronize block synchronizes two signals based on timestamps. The inputs are two signals with their respective timestamps. The Synchronize block outputs the signal values with matching timestamps, including matching timestamps from previous sampling instants. The Maximum history parameter indicates how many previous sampling instants are considered when finding matching timestamps.
 The Synchronize block must store previous values of the input signals to match timestamps
from prior sampling instants. Hence, for large input signals such as images, be careful
not to make the Maximum history parameter too high or the block will
consume a large amount of memory unnecessarily.
The Synchronize block must store previous values of the input signals to match timestamps
from prior sampling instants. Hence, for large input signals such as images, be careful
not to make the Maximum history parameter too high or the block will
consume a large amount of memory unnecessarily.
When a match is found, the
Multi-dimensional and variable-size signals are supported. Refer to Variable-Size Signals for more details on variable-size signals.
Helpful Hints
Variable-size signals
 When using the Synchronize block with variable-size signals in subsystems, make sure any
Action Port
MATLAB Command Line
Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window:
doc ActionPort;,
Enable
MATLAB Command Line
Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window:
doc Enable or
Trigger
MATLAB Command Line
Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window:
doc Trigger ports are
configured to propagate the sizes of variable-size signals during execution.
When using the Synchronize block with variable-size signals in subsystems, make sure any
Action Port
MATLAB Command Line
Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window:
doc ActionPort;,
Enable
MATLAB Command Line
Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window:
doc Enable or
Trigger
MATLAB Command Line
Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window:
doc Trigger ports are
configured to propagate the sizes of variable-size signals during execution.
Input Ports
s1
The first signal. Multi-dimensional and variable-size inputs are supported as well as arbitrary data types.
t1
A scalar input that represents the timestamp for the first signal. Only the Simulink built-in numeric data types are supported. The timestamp need not represent wall-clock time but must be monotonically increasing with time.
s2
The second signal. Multi-dimensional and variable-size inputs are supported as well as arbitrary data types.
t2
A scalar input that represents the timestamp for the second signal. Only the Simulink built-in numeric data types are supported. The timestamp need not represent wall-clock time but must be monotonically increasing with time.
Output Ports
s1
The value of the first signal when the timestamp of the first and second input signal match.
t1
The timestamp of the first signal at the time of the match.
s2
The value of the second signal when the timestamp of the first and second input signal match.
t2
The timestamp of the second signal at the time of the match.
new
A Boolean output indicating whether a match was found. This output goes to one when a match is found during the current sampling instant. Otherwise it is zero.
Data Type Support
The Synchronize block accepts signals of any of the built-in Simulink datatypes, except fixed point, for the signal inputs, s1 and s2. Multi-dimensional and variable-size signals are supported. See Variable-Size Signals for more information on variable-size signals.
The timestamp inputs only accept the built-in Simulink numeric datatypes.
Parameters and Dialog Box
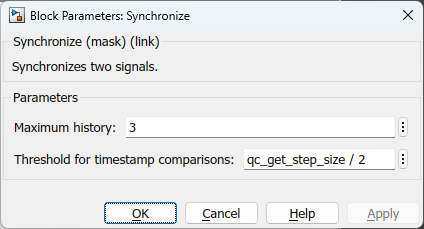
Maximum history
The maximum number of samples of the input to buffer in order to find a match. Note that for large input signals, such as images, the amount of memory used is directly proportional to the magnitude of this parameter.
Threshold for timestamp comparisons
Timestamps may be floating-point or may not represent wall-clock time. Hence, the threshold parameter may be used to indicate what constitutes equality when comparing two timestamps. Formally, two timestamps are considered equal when:
|t1 - t2| <= threhold
Since the comparison is less than or equal to then a threshold value of zero
is legitimate. However, for floating-point timestamps, which have inherent
inaccuracies, a non-zero threshold such as qc_get_step_size / 2
is recommended.
Targets
|
Target Name |
Compatible* |
Model Referencing |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Last fully supported in QUARC 2018. |
|
|
Rapid Simulation (RSIM) Target |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
S-Function Target |
No |
N/A |
Old technology. Use model referencing instead. |
|
Normal simulation |
Yes |
Yes |

Copyright ©2025 Quanser Inc. This page was generated 2025-11-01. Submit feedback to Quanser about this page.
Link to this page.