

Vision Sobel Edge

|
This block is currently a beta version. If you are using this block, we would appreciate any feedback at tech@quanser.com. |
Detects edges on the input image using Sobel kernel.
Library
QUARC Targets Beta/Image Processing/Open Source Computer Vision MATLAB Command Line Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window: qc_open_library('quarc_library_beta/Image Processing/Open Source Computer Vision')
Description
The Vision Sobel Edge block finds the edges on the input image and marks them in the output image using Sobel operator.
In order to use this block, be sure to follow the instructions described on the Vision Capture Image page, and take careful note of the limitations.
Input Ports
src_image
A handle to a source image that uses OpenCV (Open Source Computer Vision) IplImage structure.
Output Ports
edge_image
A grayscale image that marks the edges of input image in 8-bit format.
dst_image
Thresholded destination image in 8-bit gray or binary format.
err
An error signal which is negative in case of invalid memory allocation or usage of invalid parameter values.
Parameters and Dialog Box
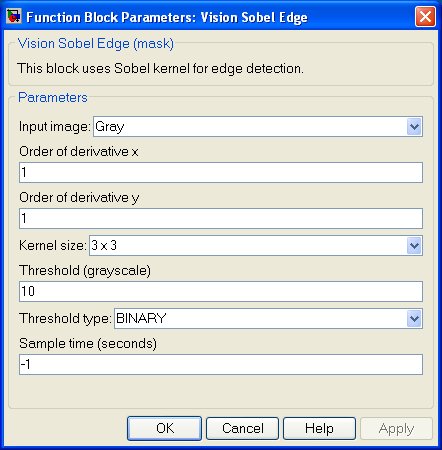
Input image
Specifies the type of input image to be used for edge detection. The available options are Gray, Blue,
Green, and Red. If the input image is a color image, this block either converts it into a grayscale image
or splits it into red, green, or blue color plane according to the specified parameter. On the other hand, if the input
is a grayscale or binary image, the edge detection algorithm is directly applied to it.
Order of derivative x
Specifies the order of derivative x.
Order of derivative y
Specifies the order of derivative y.
Kernel size
Specifies a kernel size of Sobel operator to be convolved with the input image. The Sobel operators combine Gaussian smoothing
and differentiation for noise reduction. Gaussian smoothing, however, is not incorporated for kernel size 3×1 or 1×3.
The following examples show Sobel operators for kernel size 3×3.
If Order of derivative x = 1 and Order of derivative y = 0, the operator is defined as
|-1 0 1|
|-2 0 2| .
|-1 0 1|
If Order of derivative x = 0 and Order of derivative y = 1, the operator is defined as
|-1 -2 -1|
| 0 0 0|
| 1 2 1|
or
| 1 2 1|
| 0 0 0| .
|-1 -2 -1|
The image derivative is calculated by convolving the image with the appropriate kernel:
edge_image(x,y) = dxorder+yordersrc_image/dxxorder•dyyorder |(x,y)
Threshold
Specifies a grayscale value for thresholding operation.
Threshold type
Specifies the type of thresholding to be used. The options are BINARY, BINARY_INV, TRUNC, TOZERO,
and TOZERO_INV. The options are described as follows:
BINARY:
dst_image(x,y) = 255, if edge_image(x,y) > Threshold
0, otherwise
BINARY_INV:
dst_image(x,y) = 0, if edge_image(x,y) > Threshold
255, otherwise
TRUNC:
dst_image(x,y) = threshold, if edge_image(x,y) > Threshold
edge_image(x,y), otherwise
TOZERO:
dst_image(x,y) = edge_image(x,y), if edge_image(x,y) > Threshold
0, otherwise
TOZERO_INV:
dst_image(x,y) = 0, if edge_image(x,y) > Threshold
edge_image(x,y), otherwise
Sample time
The sample time of the block. A sample time of 0 indicates that the block will be treated as a continuous time block. A positive sample time indicates that the block is a discrete time block with the given sample time. A sample time of -1 indicates that the block inherits its sample time.
Targets
|
Target Name |
Compatible* |
Model Referencing |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
No |
No |
Not supported. |
|
|
No |
No |
Not supported. |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
No |
No |
Not supported. |
|
|
Rapid Simulation (RSIM) Target |
No |
No |
Not supported. |
|
S-Function Target |
No |
N/A |
Old technology. Use model referencing instead. |
|
Normal simulation |
Yes |
Yes |
See Also

Copyright ©2025 Quanser Inc. This page was generated 2025-11-01. Submit feedback to Quanser about this page.
Link to this page.