

Wiimote
 The Wiimote block has been deprecated because of difficulties in configuring a
Bluetooth dongle to interface to the device. Achieving reliable operation often requires manual
installation of a Bluetooth stack, for which the version and vendor are highly dependent on
the Bluetooth dongle selected. Therefore, this device has been deprecated as too unwieldy to support.
The Wiimote block has been deprecated because of difficulties in configuring a
Bluetooth dongle to interface to the device. Achieving reliable operation often requires manual
installation of a Bluetooth stack, for which the version and vendor are highly dependent on
the Bluetooth dongle selected. Therefore, this device has been deprecated as too unwieldy to support.
Reads the state of a wiimote device connected to the target and outputs the buttons, accelerations, and detected IR points.
Library
QUARC Targets Deprecated/Devices/Third-Party/Nintendo/Controllers MATLAB Command Line Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window: qc_open_library('quarc_library_deprecated/Devices/Third-Party/Nintendo/Controllers')
Description
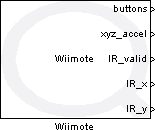
The Wiimote block reads the state of the Wii Remote (or "wiimote") on the target and outputs the button, acceleration, and IR camera information. This block provides the same functionality as the Host Wiimote block except that the block executes on the target rather than the host.
The button states are given as a vector of boolean values indicating whether a button is currently pressed (true) or not (false). Note that the coordinates and button states are valid only at the current sampling instant. The block parameters allow the user to specify the sampling time.
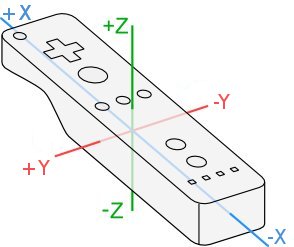
The X, Y, and Z axis accelerations are output as double-precision values and are measured in g's. A diagram of the wiimote axes is shown below.
The IR camera detects up to four points and determines the approximate
(x,y) coordinates of each point within a 1024x768 pixel image. The IR_valid
output signal is a boolean vector with four elements that indicates whether or not the
corresponding point was detected. For each detected point,
the Wiimote block will set the corresponding element in
the IR_valid output vector to true and
output the coordinates in the corresponding elements of the x and y output vectors
(IR_x and IR_y) with values ranging from 0 to 1023 and 0 to 767,
respectively; points that are not detected will have an "invalid" coordinate value of (1023, 1023) and
the corresponding IR_valid element will be set to false.
The WiiMotion Plus extension contains a 3-axis gyroscope and can be connected to the end of the Wiimote. When selected, the WiiMotion Plus block parameter will cause the Wiimote block to attempt to activate the WiiMotion Plus extension and read gyroscope data from it. Also, an additional output will appear that contains the 3-axis gyroscope data.
Installation Requirements
Hardware requirements
 In order to use the Wiimote block, a compatible Bluetooth device
must be installed on the target PC and connected to the wiimote so that the wiimote is connected
as an HID device.
This block has been tested with bluetooth devices that use
BlueSoleil drivers; please refer to your bluetooth device documentation
for instructions on installing drivers and the supported BlueSoleil versions for your device.
Instructions for connecting the wiimote to a BlueSoleil bluetooth device can be found at
https://www.instructables.com/How-To-Connect-your-Wiimote-to-your-PC-via-Blueto/.
More information on other bluetooth devices and connection procedures can be found online at
https://wiibrew.org/wiki/Main_Page, ,
or other related sites.
In order to use the Wiimote block, a compatible Bluetooth device
must be installed on the target PC and connected to the wiimote so that the wiimote is connected
as an HID device.
This block has been tested with bluetooth devices that use
BlueSoleil drivers; please refer to your bluetooth device documentation
for instructions on installing drivers and the supported BlueSoleil versions for your device.
Instructions for connecting the wiimote to a BlueSoleil bluetooth device can be found at
https://www.instructables.com/How-To-Connect-your-Wiimote-to-your-PC-via-Blueto/.
More information on other bluetooth devices and connection procedures can be found online at
https://wiibrew.org/wiki/Main_Page, ,
or other related sites.
 Note that some Bluetooth devices may not allow multiple wiimote connections simultaneously, and there may be
interoperability issues if more than one Bluetooth device is installed on the PC. If there are problems
connecting to a wiimote (particularly if multiple wiimote have been used), it is sometimes necessary to
disconnect or "unplug" the wiimote device from the bluetooth using the bluetooth software and reconnect it to
the bluetooth dongle.
Note that some Bluetooth devices may not allow multiple wiimote connections simultaneously, and there may be
interoperability issues if more than one Bluetooth device is installed on the PC. If there are problems
connecting to a wiimote (particularly if multiple wiimote have been used), it is sometimes necessary to
disconnect or "unplug" the wiimote device from the bluetooth using the bluetooth software and reconnect it to
the bluetooth dongle.
Connection procedure
 After installing the bluetooth device software, follow these steps to run the wiimote
device in Simulink:
After installing the bluetooth device software, follow these steps to run the wiimote
device in Simulink:
Input Ports
This block has no input ports.
Output Ports
buttons
An 11-element vector of boolean values representing the states of up to 11 wiimote
buttons, including the directional-pad (D-pad) buttons, but excluding the Power button.
Each element in the vector is true if the button is being
pressed at the current sampling instant and false if the button is
not being pressed at the current sampling instant. The wiimote button output vector
represents the following wiimote buttons, beginning from the first element: D-pad left,
D-pad right, D-pad down, D-pad up, A button, B button, 1 button, 2 button, + button, - button,
Home button.
xyz_accel
A three-vector of double-precision values representing the X, Y, and
Z axis accelerations, respectively. The accelerations are measured with respect to the
wiimote coordinate system shown in the above diagram, and the units are given in g's. The wiimote
is calibrated to zero acceleration in free fall. Hence, held flat and at rest, the wiimote shows
a negative acceleration in the +Z direction due to gravity.
IR_valid
A four-element vector of booleanvalues that indicates whether each point was detected and
has valid coordinates (true) or was not detected and has invalid coordinate values (false).
IR_x
A four-element vector of uint16 values representing the x coordinates
of up to four IR points detected by the wiimote IR camera. Valid values range from 0 to 1023 inclusive.
If the point is not detected the x coordinate will have a value of 1023.
IR_y
A four-element vector of uint16 values representing the y coordinates
of up to four IR points detected by the wiimote IR camera. Valid values range from 0 to 767 inclusive.
If the point is not detected the y coordinate will have a value of 1023.
xyz_gyro
A three-vector of double-precision values representing angular velocities about the X, Y, and
Z axes shown in the wiimote coordinate system above. The units of angular velocity
are given in rad/s. This output is only shown if the WiiMotion Plus parameter
is selected.
Parameters and Dialog Box
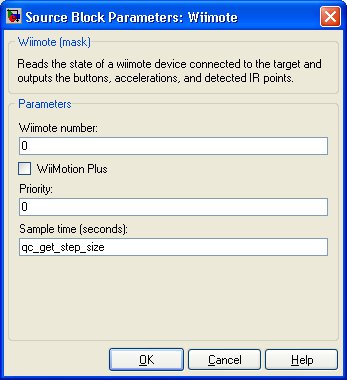
Wiimote number
This number is used to enumerate wiimotes connected to the PC. The first wiimote is 0, the second wiimote is 1, and so on.
WiiMotion Plus
If selected, the Wiimote block will attempt to activate and read data from the WiiMotion Plus extension controller. The WiiMotion Plus extension must be connected properly to the Wiimote to use this option.
Priority
The priority of the thread. In general, a value of 0 indicates the lowest priority and higher values indicate a higher priority. The number of priority levels available depends on the type of QUARC target for which code is being generated.
Sample time
The sample time of the block. A sample time of 0 indicates that the block will be treated as a continuous time block. A positive sample time indicates that the block is a discrete time block with the given sample time.
A sample time of -1 indicates that the block inherits its sample time. Since this is a source block, only inherent the sample time when it is placed in a conditionally executed subsystem, like a Triggered or Enabled Subsystem, or in a referenced model.
To use the fundamental sampling time of the model, set the sample time to qc_get_step_size, which is a QUARC function that returns the fundamental sampling time of the model.
Targets
|
Target Name |
Compatible* |
Model Referencing |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
No |
Only supported in Windows XP. |
|
|
No |
No |
||
|
No |
No |
||
|
No |
No |
||
|
No |
No |
||
|
No |
No |
||
|
No |
No |
||
|
No |
No |
||
|
No |
No |
||
|
No |
No |
||
|
No |
No |
||
|
No |
No |
||
|
No |
No |
||
|
No |
No |
Last fully supported in QUARC 2018. |
|
|
Rapid Simulation (RSIM) Target |
No |
No |
|
|
S-Function Target |
No |
N/A |
Old technology. Use model referencing instead. |
|
Normal simulation |
No |
No |
See Also

Copyright ©2025 Quanser Inc. This page was generated 2025-11-01. Submit feedback to Quanser about this page.
Link to this page.