

File Read
Reads a file from the local file system.
Library
QUARC Targets/Sources/Signals MATLAB Command Line Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window: qc_open_library('quarc_library/Sources/Signals')
Description

The File Read block reads a file from the local file system. Unlike the From File MATLAB Command Line Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window: matlab:doc('From File'); block, which reads the file at compile time, the File Read block reads the file at run time. Hence, the file must be placed on the target system at the absolute or relative path specified in the File name parameter. The File Read block is useful for reading signals recorded from other models or reading calibration data, for example.
The File Read block supports a variety of different input file formats, such as MAT-files, CSV files, text files or raw binary files. It can also skip over header lines or columns in the data. When the end of the file is reached, the last read values will be held at the output of the block. The new output indicates whether the data at the output is new or not, and may be used as an indication of when the end of file is reached. The input files may be recorded using a block such as the To Host File block.
The File Read block may be configured to read the input file multiple times by setting the Loop count parameter to a non-zero value. The loop count is the number of times the block loops back to the beginning of the file. A value of -1 is treated as infinity so that it loops continuously.
Input Ports
cls
Used to close the file. Setting this input to a non-zero value will cause the file to be closed. The file will remain closed as long as this input is non-zero. When this input is zero or false, then the file indicated by the current filename at the file input will be opened. The file will remain open as long as this input is zero and the loop count has not expired.
This input is only present when the Source of file name parameter is set to External input port.
file
A string specifying the filename to open. The string must be a null-terminated
vector of characters represented as a vector of uint8 quantities. It may be variable-sized. This string is typically provided
either directly or indirectly by a Model Argument
block or String Constant block. For more sophisticated
generation of the filename, consider the String Print block.
This input is only available when the Source of file name parameter is set to External input port. Refer to the documentation below on the Source of file name parameter for details.
Output Ports
data
One sample of data from the input file. The data type will be the data type specified in the Data type parameter.
new
A logical output that is true when new data is presented at the data output and false otherwise. This signal is typically one until the end of file is reached, at which point it goes to zero.
Data Type Support
The File Read block outputs signals of any of the built-in Simulink datatypes, except fixed point, for the data output. The data type is set using the Data type option under the Signal Data Types tab. The new output is always Boolean.
Parameters and Dialog Box
Main Pane
The Main pane of the dialog appears as follows:
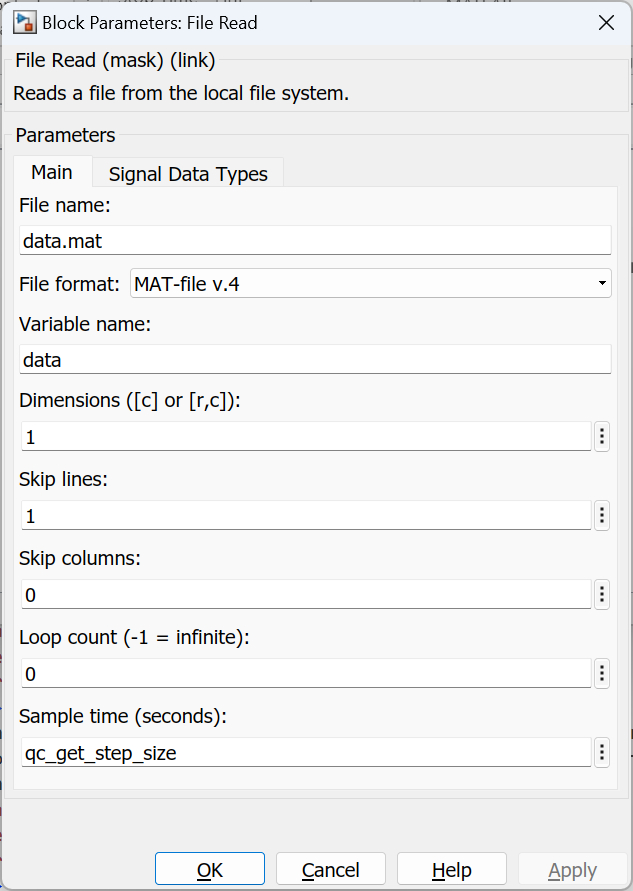
Source of file name
Indicates whether the filename should be determined from the dialog parameters or an
input port. If this field is set to Specify via dialog (do not evaluate) then
the filename is specified via the File name
parameter. In this case, the filename is not evaluated as a MATLAB expression but is
interpreted as a literal string. However, format specifiers are recognized. Refer
to qc_perform_substitutions
for a list of the format specifiers available.
 If format specifiers which change frequently, such as '%{time}' or
'%{instance}', are used in the filename then the File Read block cannot be placed
in a referenced model, because the filename will change from the time the code is built to when
the code is run. As a result, Simulink will insist that the code be rebuilt because block
parameters in referenced models are inlined. Instead, specify the source of the filename as
If format specifiers which change frequently, such as '%{time}' or
'%{instance}', are used in the filename then the File Read block cannot be placed
in a referenced model, because the filename will change from the time the code is built to when
the code is run. As a result, Simulink will insist that the code be rebuilt because block
parameters in referenced models are inlined. Instead, specify the source of the filename as
External input port and pass the filename from the top-level model. Use a
String Constant block
in the top-level model to generate the filename.
If this field is set to Specify via dialog (evaluate) then the filename is also specified
via the File name parameter. However, in this case,
the filename is evaluated as a MATLAB expression. This option is convenient for using a variable
in the MATLAB workspace for the filename.
If this field is set to External input port then the File name
parameter is ignored and an extra input port is provided which determines the filename. In
this case a cls port is also provided for closing the file and opening a
new file with the current filename at the input port.
File name (tunable offline)
The absolute or relative path to the file to read on the target as a string. If a relative path is specified then
it is relative to the current directory for the model. The current directory for a model is specified
on the Interface tab of the
Configuration Parameters dialog. In particular,
it is specified using the -d option in the MEX-file arguments.
File format
The file format of the input file. The file format is not predetermined from the file extension as different file extensions may be used. All the input file formats may be generated by the To Host File block. The supported file formats are:
|
File Format |
Description |
|---|---|
|
MAT-file v.4 |
A version 4 MAT-file containing a numeric array. For vector data, each column of the array represents a different sampling instant. The first row may represent time. To omit rows from the output, specify the number of rows to skip in the Skip lines parameter. To omit initial columns from the output, specify the number of columns to skip in the Skip columns parameter. Skipping columns represents skipping over initial samples. For example, it may be desirable to skip over the first few seconds of data as the system recorded was stabilizing. The variable in the MAT-file that is read is determined by the Variable name parameter. |
|
MAT-file v.5 |
A version 5 MAT-file containing a numeric array. For vector data, each column of the array represents a different sampling instant. The first row may represent time. To omit rows from the output, specify the number of rows to skip in the Skip lines parameter. To omit initial columns from the output, specify the number of columns to skip in the Skip columns parameter. Skipping columns represents skipping over initial samples. For example, it may be desirable to skip over the first few seconds of data as the system recorded was stabilizing. The variable in the MAT-file that is read is determined by the Variable name parameter. |
|
CSV file |
A comma-separated variable file containing a numeric array. A CSV file is a text file where each line represents a sample, and each row represents a different sampling instant. Values are separated by commas and may be in quotes. CSV files often start with header rows. To skip over these header rows, specify the number of lines to bypass in the Skip lines parameter. To omit the first columns of the data (such as time), specify the number of columns to skip in the Skip columns parameter. The Variable name parameter is not used for this file format because only one variable may be stored in the CSV file. |
|
Text file |
A text file containing a numeric array in which each line represents a sample, and each row represents a different sampling instant. Values are separated by whitespace and should not be quoted. Text files often start with header rows. To skip over these header rows, specify the number of lines to bypass in the Skip lines parameter. To omit the first columns of the data (such as time), specify the number of columns to skip in the Skip columns parameter. The Variable name parameter is not used for this file format because only one variable may be stored in the text file. |
|
Raw binary file |
A raw binary file containing a numeric array stored in binary form. The data type of the binary data is determined by the Data type parameter. Each sampling instant is stored in column-major order, with the matrix for each sampling instant following one after the other. To skip over columns in each sampling instant, such as time, specify the number of colums to bypass in the Skip columns parameter. The Variable name parameter is not used for this file format because only one variable may be stored in the raw binary file. |
Variable name
The name of the variable to read in the MAT-file as a string. This parameter is only used for MAT-files, which may store more than one variable in a single file. If the variable is not found the block will issue an error.
Dimensions
The dimensions of the output. The dimensions should reflect the input file being read. If rows or columns of the data are being skipped, the sum of the dimensions and number of rows or columns being skipped cannot exceed the dimensions of the data stored in the MAT-file or an error will be issued.
The dimensions are usually just a scalar indicating that the output is a vector. If two dimensions are specified then a matrix will be read from the input file and that matrix will be output each sampling instant.
Skip lines (tunable offline)
The number of lines or rows to skip in the input file. For CSV or text files, this parameter indicates the number of header rows to skip. For MAT-files, it denotes the number of rows in each sampling instant to skip over (such as time data).
Skip columns (tunable offline)
The number of columns to skip in the input file. For CSV, text or raw binary files, this parameter indicates the number of initial columns to skip, such as time data. For MAT-files, it denotes the number of columns to skip over, which represents initial sampling instants.
Loop count (tunable online)
The number of times the block should loop back to the beginning of the file when it reaches the end of file. The default value is zero so that it only reads the file once. A value of -1 causes it to loop indefinitely. The loop count may be changed on the fly, but will only take effect if the current operation is not complete.
Sample time
The sample time of the block. A sample time of 0 indicates that the block will be treated as a continuous time block. A positive sample time indicates that the block is a discrete time block with the given sample time.
A sample time of -1 indicates that the block inherits its sample time. Since this is a source block, only inherent the sample time when it is placed in a conditionally executed subsystem, like a Triggered Subsystem, Enabled Subsystem, Function Call Subsystem or in a referenced model.
To use the fundamental sampling time of the model, set the sample time to qc_get_step_size, which is a QUARC function that returns the fundamental sampling time of the model.
The default sample time is set to qc_get_step_size.
Signal Data Types Pane
The Signal Data Types pane of the dialog appears as follows:
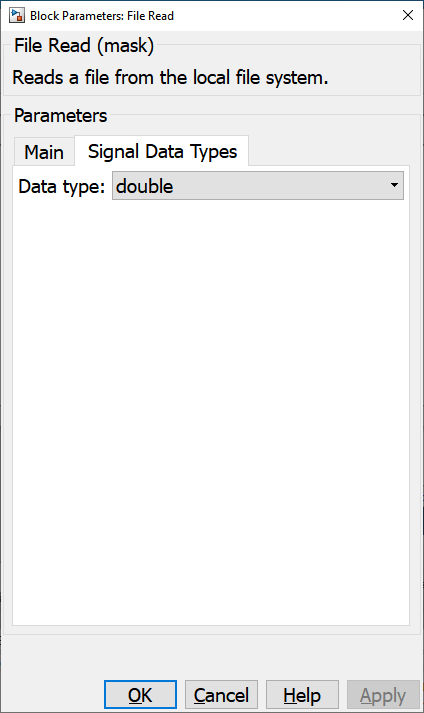
Data type
The data type of the output. For raw binary files, this parameter also indicates the data type of the binary data in the input file.
Targets
|
Target Name |
Compatible* |
Model Referencing |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Last fully supported in QUARC 2018. |
|
|
Rapid Simulation (RSIM) Target |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
S-Function Target |
No |
N/A |
Old technology. Use model referencing instead. |
|
Normal simulation |
Yes |
Yes |

Copyright ©2025 Quanser Inc. This page was generated 2025-11-01. Submit feedback to Quanser about this page.
Link to this page.