

HIL Read Analog Codes
Reads the specified analog channels immediately, returning the raw integer codes from the analog-to-digital converters.
Library
QUARC Targets/Data Acquisition/Generic/Immediate I/O MATLAB Command Line Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window: qc_open_library('quarc_library/Data Acquisition/Generic/Immediate I//O')
Description

The HIL Read Analog Codes block reads the specified analog channels every time the block is executed. The channels are read immediately. The output is the raw codes from the analog-to-digital converters. The meaning of the integral codes depends on the hardware. This block is useful for prototyping fixed-point control algorithms and for teaching purposes.
Input Ports
This block has no input ports.
Output Ports
The number of output ports depends on the Vector output parameter. If this option is checked then the output is a vector containing the raw integer codes read from the channels specified in the Channels parameter. Otherwise there is one output port for each channel and each port outputs the raw integer code read from the corresponding channel. Refer to the documentation on the Vector output parameter below for more details.
Data Type Support
The HIL Read Analog Codes block outputs signals of type int32, uint32 or double.
See the Signal Data Types pane below for information on how the output data type is determined.
Parameters and Dialog Box
Individual Panes
Main Pane
The Main pane of the dialog appears as follows:
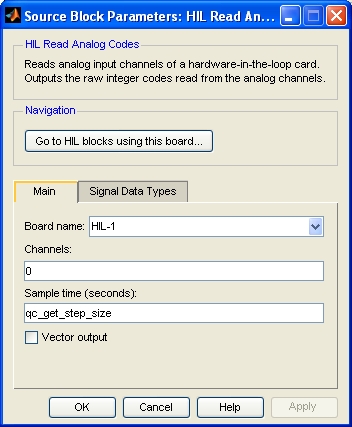
Board Name
The name of the board whose analog channels will be read. Boards are configured using the HIL Initialize block. Place an HIL Initialize block in your diagram to add a board name to the list.
Channels
The analog channels to read. The number of channels available depends on the board selected. Refer to Channels for more information.
Select a board type from the list for board-specific details:
Sample time
The sample time of the block. A sample time of 0 indicates that the block will be treated as a continuous time block. A positive sample time indicates that the block is a discrete time block with the given sample time.
A sample time of -1 indicates that the block inherits its sample time. Since this is a source block, only inherent the sample time when it is placed in a conditionally executed subsystem, like a Triggered or Enabled Subsystem, or in a referenced model.
The default sample time is set to qc_get_step_size, which is a QUARC function that returns the fundamental sampling time of the model. Hence, the default sample time is a discrete sample time with the same sampling time as the fixed step size of the model.
Vector output
If this option is checked then the block will have a single vector output with one element in the vector for each channel. The raw integer codes read from each channel will appear in the vector in the same order as the channels in the Channels parameter.
If this option is not checked then the block will have one output for each channel. The output ports will appear in the same order as the channels in the Channels parameter. Each port will be labeled with the corresponding channel number.
Signal Data Types Pane
The Signal Data Types pane of the dialog appears as follows:
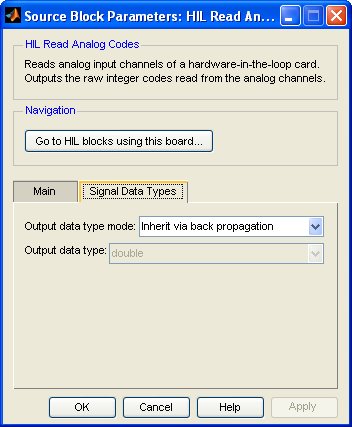
Output data type mode
Sets the data type of the output to be inherited by back propagation or to be specified explicitly in the dialog.
If back propagation is selected then the data type of the output will be determined
by the block to which the output is connected. If the output is not connected or
it is connected to a block which supports multiple datatypes, then the output data
type will be double.
Otherwise the data type of the output can be specified explicitly using the Output data type parameter.
Output data type
Sets the data type of the output explicitly.
Targets
|
Target Name |
Compatible* |
Model Referencing |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
No |
No |
Not supported. |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
Last fully supported in QUARC 2018. |
|
|
Rapid Simulation (RSIM) Target |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
S-Function Target |
No |
N/A |
Old technology. Use model referencing instead. |
|
Normal simulation |
Yes |
Yes |
Due to safety and liability concerns, the hardware may not be accessed during normal simulation. |
See Also

Copyright ©2025 Quanser Inc. This page was generated 2025-11-01. Submit feedback to Quanser about this page.
Link to this page.