

Multiwii Write RC
Writes raw RC values to the auto-pilot.
Library
QUARC Targets/Communications/Multiwii MATLAB Command Line Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window: qc_open_library('quarc_library/Communications/Multiwii')
Description

The Multiwii Write RC block uses the Multiwii protocol on the input stream to send a command to the aircraft to
write raw RC values to the auto-pilot. The Multiwii Write RC block sends a MSP_SET_RAW_RC
message to the auto-pilot.
This block is designed to be used with blocking I/O. It is typically used with a stream connected to a serial port. To open the stream a Multiwii Connect block should be used.
The input of the block is a vector of RC values. The units depend on the Input units parameter. The order of the RC channels in the vector depends on the auto-pilot but the first eight channels are typically roll, pitch, throttle, yaw, auxiliary 1, auxiliary 2, auxiliary 3 and auxiliary 4, in that order.
In order for the RC channels to be recognized by the auto-pilot, the auto-pilot receiver must be set to MSP RX input (control via MSP port). Also, the auxiliary 1 channel is typically used for arming a quadrotor. For example, start with low throttle (third RC channel) and then switch the auxiliary 1 channel from a low value to a high value (e.g. 1000 to 2000) to arm. At that point, the throttle can be increased.
A copy of the stream is also output so that the Multiwii blocks may be chained together.
If an error occurs, then the block returns a negative error code at its err output. The Compare to Error block may be used to check for specific error codes. If the stream is not valid because it is not yet connected, the err output will be zero since this condition is expected and the validity of the stream may be checked using the con output of the Multiwii Connect block.
Limitations
Minimum execution frequency
 The Multiwii Write RC block must be called at least once a second or the auto-pilot will revert
to default RC values, which are typically low throttle.
The Multiwii Write RC block must be called at least once a second or the auto-pilot will revert
to default RC values, which are typically low throttle.
Helpful Hints
Other uses of this block
 Although it is intended for use in the main diagram with the other Multiwii
blocks, the
Multiwii Write RC
block may be used
with the Advanced stream blocks, even in an asynchronous thread.
Although it is intended for use in the main diagram with the other Multiwii
blocks, the
Multiwii Write RC
block may be used
with the Advanced stream blocks, even in an asynchronous thread.
Input Ports
stm
A reference to the stream created by the Multiwii Connect block. If a connection has not yet been established, then the err output of the Multiwii Write RC block will be zero.
rc
This input depends on the Input units parameter. Each element of the input vector corresponds to a separate RC channel. However the data type and range changes depending on the input units. Refer to the Input units parameter for details.
The input vector may be fixed or variable-sized.
Output Ports
stm
A reference to the stream. This output is merely a copy of the stm input. Providing this output makes it much easier to establish the execution order of Multiwii blocks in the diagram because Simulink generally executes daisy-chained blocks in sequence.
err
An int32 value indicating whether the message was sent successfully. This value will be positive if message was sent successfully. It will be zero if no message was sent. If an error occurs then this value is a negative error code. See Error Codes for the different error codes and their values. Use the Compare to Error block rather than the error code itself to check for specific error codes. To check for errors in general use the Compare to Zero block to check whether the err output is less than zero.
Parameters and Dialog Box
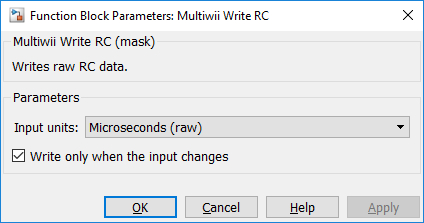
Input units
This parameter determines the data type and units of the rc input. The table below shows the input for each of the different units:
|
Units |
Data Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Bipolar percentage |
double |
Each element maps the input range of [-1,1] to the typical [1000,2000] range such that -1 becomes 1000, 0 becomes 1500 and 1 becomes 2000. Any values outside this range are mapped according to the same affine transformation. These units are useful when the RC data represent -100% to 100% throttle. |
|
Unipolar percentage |
double |
Each element maps the input range of [0,1] to the typical [1000,2000] range such that 0 becomes 1000 and 1 becomes 2000. Any values outside this range are mapped according to the same affine transformation. These units are useful when the RC data represent 0 to 100% throttle. |
|
Seconds |
double |
Each element maps the input range of [0.001,0.002] to the typical [1000,2000] range such that 0.001 becomes 1000 and 0.002 becomes 2000 so that the input is the RC pulse width in seconds. Any values outside this range are mapped according to the same affine transformation. These units are useful when the RC data are being used to drive PWM pulse widths via the HIL blocks. |
|
Microseconds (raw) |
uint16 |
Each element is the raw RC value, which is the RC pulse width in microseconds. |
Targets
|
Target Name |
Compatible* |
Model Referencing |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Last fully supported in QUARC 2018. |
|
|
Rapid Simulation (RSIM) Target |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
S-Function Target |
No |
N/A |
Old technology. Use model referencing instead. |
|
Normal simulation |
Yes |
Yes |
See Also

Copyright ©2025 Quanser Inc. This page was generated 2025-11-01. Submit feedback to Quanser about this page.
Link to this page.