MATLAB Command Line
Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window:
quarc_advanced_nonblocking_server_demo; quarc_advanced_nonblocking_client_demoQUARC Advanced Communications Demo - Non-Blocking Mode
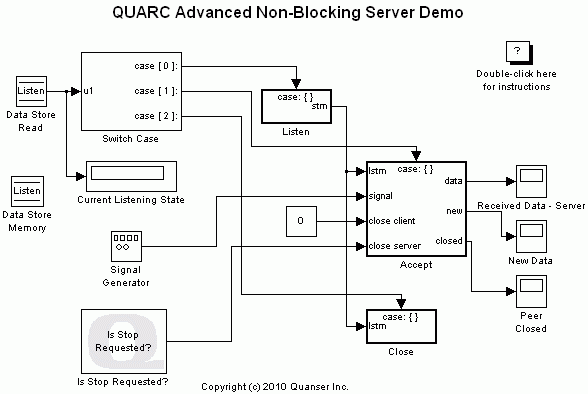
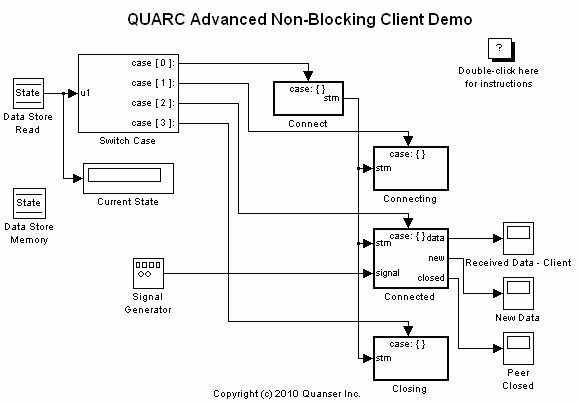
This example consists of two Simulink models; a server and a client. It demonstrates how to use the Advanced Communications blockset from the QUARC Targets Library to establish a connection in non-blocking mode between two Simulink models. For a detailed description of these models and how they operate, please refer to the Advanced Communications - Non-Blocking Mode section of the QUARC documentation. For general information on Advanced Communications feature of QUARC, you can refer to the Advanced Communications section.

Configuring the Demonstration
To set up the demonstration, double-click on the "Listen" subsystem in the quarc_advanced_nonblocking_server_demo.mdl model. Next, double-click on the Stream Listen block. Also, double-click on the "Connect" subsystem in the quarc_advanced_nonblocking_client_demo.mdl model. Next, double-click on the Stream Connect block. Now, make sure the URI upon which to listen parameter of Stream Listen block is the same as the URI of host to which to connect parameter of the Stream Connect block.
Demonstration
Building, deploying and starting the models
Refer to One Step Process in QUARC Basic Procedures to build, deploy and start each model.
Note that the order in which you start the models is not important. However, in practical situations, the server side should always be running before the client starts.
 In the case of using UDP as the communication protocol, it's necessary to start the server prior to the client. The reason is UDP does not
establish a connection between client and server, and server relies on the IP address of its received packages to communicate. When the client
is started, it sends a data package to the server, and because of its blocking design, it waits for a reply from the server which has
not been started yet. In the other hand, when the server is started, it waits for a package from the client to know the IP address of the client.
Therefore, both parties wait for each other, and no data is communicated.
In the case of using UDP as the communication protocol, it's necessary to start the server prior to the client. The reason is UDP does not
establish a connection between client and server, and server relies on the IP address of its received packages to communicate. When the client
is started, it sends a data package to the server, and because of its blocking design, it waits for a reply from the server which has
not been started yet. In the other hand, when the server is started, it waits for a package from the client to know the IP address of the client.
Therefore, both parties wait for each other, and no data is communicated.
This problem can be solved when the client is running on Windows. The solution is to add in front of the client URI. In this case, when server is unreachable an error signal is created internally, and the client tries to send the starting data package again. Therefore, when the server is started, it eventually receives a data package from the client making it leave its listening state, and start the communication.
Running the model
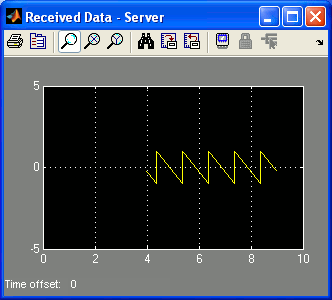
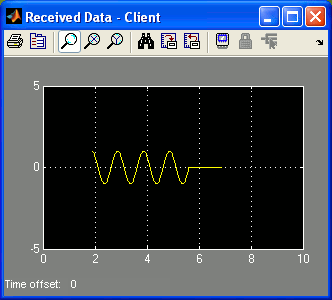
Double-click on the "Received Data - Server" Scope block in the quarc_advanced_nonblocking_server_demo.mdl model to open the Scope. Do the same for the "Received Data - Client" Scope block in the quarc_advanced_nonblocking_client_demo.mdl model to open that Scope as well.
A sawtooth wave of amplitude 1 will appear in the "Received Data - Server" Scope. Meanwhile, the "Received Data - Client" Scope traces a sine wave of amplitude 1. The server model sends a sine wave to the client model while the client model sends a sawtooth wave to the server model.
Stopping the models
Refer to One Step Process in QUARC Basic Procedures to stop each model.
Running the example on a different target
To run the example on a different target, refer to the instructions on the Running QUARC Examples on Remote Targets page.
If the quarc_advanced_nonblocking_server_demo.mdl and the quarc_advanced_nonblocking_client_demo.mdl model are being run on different targets, then the URI of the Stream Connect block in the client model should use the host name or IP address of the machine running the server for the hostname of its URI. For example, if the server is running on a machine with IP address 192.168.0.16 and the URI of the Stream Listen block in the server model is tcpip://localhost:18000, then the URI of the Stream Connect block in the client model should be tcpip://192.168.0.16:18000.
Copyright ©2025 Quanser Inc. This page was generated 2025-11-01. Submit feedback to Quanser about this page.
Link to this page.