

Roomba Drive
Controls Roomba's motion using the specified velocity and direction.
Library
QUARC Targets/Devices/Third-Party/iRobot/Roomba/Interfacing MATLAB Command Line Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window: qc_open_library('quarc_library/Devices/Third-Party/iRobot/Roomba/Interfacing')
Description

The Roomba Drive block controls Roomba's drive wheel. It takes two inputs. The first input specifies the average velocity of the drive wheels in millimeters per second (mm/s). The second input specifies the radius in millimeters at which Roomba will turn. The longer radii make Roomba drive straighter, while the shorter radii make Create turn more. The radius is measured from the center of the turning circle to the center of Roomba. A Drive command with a positive velocity and a positive radius makes Roomba drive forward while turning toward the left. A negative radius makes Roomba turn toward the right. A negative velocity makes Roomba drive backward.
This command is available in Safe, or Full operating mode of Roomba (see Roomba Modes block). Execution of this command does not change current Roomba operating mode.
Important Notes
 Use System Timebase
block in Normal simulation.
Use System Timebase
block in Normal simulation.
Input Ports
rmb
A reference to the Roomba stream (see Roomba Initialize block).
vel
16-bit signed velocity in mm/s. The maximum forward and backward velocities are 500 mm/s and -500 mm/s, respectively.
rad
16-bit signed radius of curvature in mm. The maximum counterclockwise and clockwise radii of curvature are 2000 mm and -2000 mm, respectively.
Special cases:
Output Ports
rmb
A reference to the Roomba stream, which is the same as input Roomba stream reference. It helps creating a daisy chain of Roomba blocks.
err
This signal returns a negative value in case of memory allocation error or data communication error through Roomba serial port.
Parameters and Dialog Box
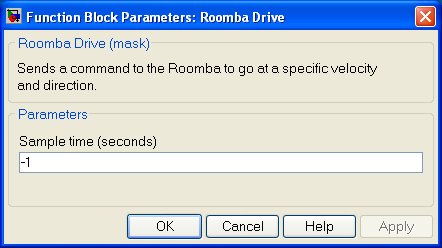
Sample time
The sample time of the block. A sample time of 0 indicates that the block will be treated as a continuous time block. A positive sample time indicates that the block is a discrete time block with the given sample time. A sample time of -1 indicates that the block inherits its sample time.
Targets
|
Target Name |
Compatible* |
Model Referencing |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Last fully supported in QUARC 2018. |
|
|
Rapid Simulation (RSIM) Target |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
S-Function Target |
No |
N/A |
Old technology. Use model referencing instead. |
|
Normal simulation |
Yes |
Yes |
Use System Timebase. |
See Also

Copyright ©2025 Quanser Inc. This page was generated 2025-11-01. Submit feedback to Quanser about this page.
Link to this page.