

Stream Read
Receives data over a stream. This block is intended for use in the main diagram.
Library
QUARC Targets/Communications/Intermediate MATLAB Command Line Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window: qc_open_library('quarc_library/Communications/Intermediate')
Description

The Stream Read block receives data over a stream. The operation of this block is affected by the blocking mode of the stream connected to its input. Streams have two modes: blocking (the default) and non-blocking. If a Stream Call or Stream Answer block is used to create the stream, then the stream will be non-blocking. If a Stream Connect or Stream Accept block is used to create the stream then the blocking mode of the stream is determined by the Stream Connect or Stream Listen block.
This block receives values over a client stream, where the size and data type of the signal is determined by the Output data type and Dimensions parameters of the block. If the stream has been configured to swap bytes then this block will swap the order of the bytes within each element that it reads before writing them to its data output. Multi-dimensional and bus signals are supported.
Since the Intermediate Stream blocks are non-blocking, this block does not wait. If fewer bytes are available than the size of the output signal then the new output will be zero (false). If all the data requested is available then the new output will be non-zero (true). The err output will be 0, indicating that no errors occurred.
If the connection has been closed gracefully by the peer then it sets cls to a non-zero (true) value and returns zero (false) at its new output once there are fewer bytes left to read than the size of the output signal. Otherwise the cls output is zero and the new output returns true (non-zero). Once there are fewer bytes left in the stream buffer than the size of the output data vector then it sets cls to true to indicate the connection has been closed. A graceful closure of the connection by the peer is not considered an error, so the err output is zero in this case.
If an error occurs, then the block returns a negative error code at its err output. The Compare to Error block may be used to check for specific error codes. If the stream is not valid because it is not yet connected, the err output will be zero since this condition is expected and the validity of the stream may be checked using the con output of the Stream Call or Stream Answer blocks.
This block does not support two threads calling Stream Read at the same time. However, Stream Read may be called by another thread at the same time as Stream Write.
Helpful Hints
Other uses of this block
 Although it is intended for use in the main diagram with the other Intermediate
stream blocks, the Stream Read block may be used
with the Advanced stream blocks, even in an asynchronous thread.
Although it is intended for use in the main diagram with the other Intermediate
stream blocks, the Stream Read block may be used
with the Advanced stream blocks, even in an asynchronous thread.
Variable-size signals
 When using the Stream Read block with variable-size signals in subsystems, make sure any
Action Port
MATLAB Command Line
Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window:
doc ActionPort;,
Enable
MATLAB Command Line
Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window:
doc Enable or
Trigger
MATLAB Command Line
Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window:
doc Trigger ports are
configured to propagate the sizes of variable-size signals during execution. Refer to
Variable-Size Signals for more information
on variable-size signals.
When using the Stream Read block with variable-size signals in subsystems, make sure any
Action Port
MATLAB Command Line
Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window:
doc ActionPort;,
Enable
MATLAB Command Line
Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window:
doc Enable or
Trigger
MATLAB Command Line
Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window:
doc Trigger ports are
configured to propagate the sizes of variable-size signals during execution. Refer to
Variable-Size Signals for more information
on variable-size signals.
Input Ports
stm
A reference to the stream created by the Stream Call or Stream Answer block. If these blocks have not established a connection the err output of the Stream Read block will be zero.
Output Ports
stm
A reference to the stream. This output is merely a copy of the stm input. Providing this output makes it much easier to establish the execution order of Stream blocks in the diagram because Simulink generally executes daisy-chained blocks in sequence.
data
The data read from the stream buffer. The output signal is treated as an atomic
unit. It will never read part of the data from the stream buffer. These semantics
make it much easier to deal with streams in Simulink where it is difficult to deal
with "parts" of a signal. Note that the buffer size for the stream must be at least
as large as the output data or -QERR_STREAM_BUFFER_TOO_SMALL
is returned by the err output. Multi-dimensional and variable-size
signals, as well as bus signals are supported. See
Using Bus Objects with QUARC
for more information on bus signals.
new
Indicates whether the value(s) presented at the data port represent newly received data from the peer. If this output is zero (false) then no data has been received from the peer in this sampling instant.
cls
Indicates whether the connection has been closed by the peer. This output is non-zero (true) when the remote host gracefully closes the connection. Otherwise it is zero (false).
err
An int32 value indicating whether the data was read from the stream buffer successfully. This value will be 1 if data was read successfully. It will be zero if data could not be read immediately. If an error occurs then this value is a negative error code. If the connection is closed and not enough data is left in the stream buffer for the output signal then 0 is also returned. If the connection is closed but there is enough data in the stream buffer then this output returns 1. Zero is only returned once the stream buffer is exhausted. See Error Codes for the different error codes and their values. Use the Compare to Error block rather than the error code itself to check for specific error codes. To check for errors in general use the Compare to Zero block to check whether the err output is less than zero.
Data Type Support
The Stream Read block supports signals of any of the built-in Simulink data types at its data output. Multi-dimensional and variable-size signals are supported. Fixed point is not currently supported. See Variable-Size Signals for more information on variable-size signals.
The Stream Read block also supports bus signals at its data output. Buses are useful for receiving a mix of different data types in a single read operation. Use the Simulink Bus Editor to create a Simulink.Bus MATLAB Command Line Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window: doc('Simulink.Bus') object defining the bus. Then pass the name of this object in the Output type name parameter. It is convenient to save the bus object to a MAT file and then ensure that the bus object is always defined by loading this MAT file within the InitFcn callback of the Simulink model. See Using Bus Objects with QUARC for more information on bus signals.
Parameters and Dialog Box
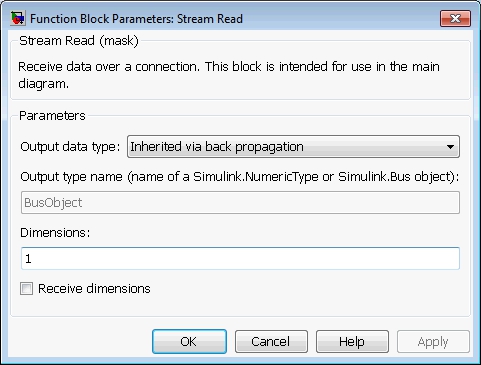
Output data type
The data type of the data output. This parameter
determines the data type of the elements that are read from the stream. If this
parameter is set to Inherited via back propagation then the data type
of the output is determined by the block connected to the data
output.
If this field is set to Specify via dialog then the Output type name
parameter is used to define the data type of the output. Refer to the Output type name
parameter for details.
Output type name
This parameter should be the name of a variable in the MATLAB workspace that defines the
data type of the output. This variable may be a Simulink.AliasType, Simulink.NumericType,
Simulink.StructType or Simulink.Bus object. Simulink.Bus objects may be
created using the Simulink Bus Editor, available from the menu of the
Simulink diagram.
|
Set the Dimensions field to |
Dimensions
The dimensions of the output data. This parameter determines how
many elements are read from the stream and the dimensions of the data
at the data output of the block. It may be a vector
with each element being at least 1. For example, to specify a 3-vector,
specify 3 as the Dimensions parameter.
To output a 2x3 matrix, enter [2, 3].
This field should be 1 when using a bus output.
For variable-sized signals, this parameter specifies the maximum dimensions of the output signal. The dimensions should match the maximum dimensions of the signal on the peer side.
Receive dimensions
This option is used with variable-sized signals. Checking this option causes the current dimensions of the output signal to be read from the stream prior to the data itself. The output signal is then sized according to the received dimensions. The block automatically determines the type of integer required for each dimension based on the maximum dimensions of the output signal specified in the Dimensions parameter. For example, if the maximum size of a dimension is less than 256 then a single 8-bit integer is received for that dimension. If the maximum size is less than 65536 then a 16-bit integer is used. Dimensions larger than 32-bits are not supported. Refer to Variable-Size Signals for more information on variable-size signals.
Targets
|
Target Name |
Compatible* |
Model Referencing |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Last fully supported in QUARC 2018. |
|
|
Rapid Simulation (RSIM) Target |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
S-Function Target |
No |
N/A |
Old technology. Use model referencing instead. |
|
Normal simulation |
Yes |
Yes |
If the Stream Call or Stream Answer block which created the stream is not active during normal simulation, then the Stream Read block does nothing. Otherwise it reads the data from the stream. |
See Also

Copyright ©2025 Quanser Inc. This page was generated 2025-11-01. Submit feedback to Quanser about this page.
Link to this page.