

Mavlink Initialize
Establishes connections to Mavlink-based flight controllers. This block is intended for use in the main diagram.
Library
QUARC Targets/Communications/Mavlink MATLAB Command Line Click to copy the following command line to the clipboard. Then paste it in the MATLAB Command Window: qc_open_library('quarc_library/Communications/Mavlink')
Description

The Mavlink Initialize block is able to act as a client or server. As a client, it connects to a flight controller, typically using TCP/IP or a serial connection. As a server, it listens for and accepts a connection from one or more flight controllers. In both cases, it uses non-blocking I/O. Non-blocking I/O is used so that the I/O does not interfere with the sample rate of the model. However, as a result, communication protocols that do not support non-blocking I/O are not supported by the Mavlink blocks.
The Connection type parameter is used to select whether the block acts as a client or server. A client connection is typically used with the TCP/IP or serial protocols to connect to a single flight controller. A server connection is typically used with UDP to allow the Mavlink blocks to interface to multiple drones simultaneously, for cooperative or swarm applications.
When using a client connection, the first time the block executes it begins to connect to the remote host. It does not wait for the connection to be established, but continues the connection process in the background. Once a connection is established, the other Mavlink blocks will begin to communicate with the client flight controller.
The client connection is maintained as long as the cls input remains zero or false. If the cls input becomes
non-zero then it closes the connection. When the cls input returns to zero then it reestablishes a connection as it
did in the beginning. Note that the connection will not be established the first time the block executes if the cls
input is non-zero at that time. When the block is not connected to a flight controller then the other Mavlink blocks
will not communicate with the flight controller.
When acting as a server, the first time the block executes it begins listening for and accepting connections from flight controllers. The block does not wait for flight controllers to connect, but accepts connections in the background. Once a connection is established, the other Mavlink blocks are able to communicate.
The server continues to listen as long as the cls input remains zero or false. If the cls
becomes non-zero then it closes any connections and stops listening. When the cls input returns to zero then it
returns to listening for connections, as it did in the beginning. Note that it will not act as a server the first time the block executes
if the cls input is non-zero at that time. When the block is not connected to a flight controller then the other Mavlink blocks
will not communicate with the flight controller(s).
Note that whether the block is acting as a client or server, it maintains a persistent connection. In other words, if the connection to a flight controller is lost then it will automatically attempt to reconnect, provided the cls input is zero.
The current state of the connection is output at the con port. The states and their integral values are:
|
Connection State |
Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
MAVLINK_STATUS_NOT_CONNECTED |
0 |
The block is neither connected nor listening for connections. |
|
MAVLINK_STATUS_CONNECTING |
1 |
The block is either connecting to or listening for and attempting to accept a connection from a flight controller but is not yet ready for communications. |
|
MAVLINK_STATUS_CONNECTED |
2 |
The block is fully connected and communication may occur over the stream. For connectionless protocols like UDP, "connected" means it is accepting UDP datagrams. |
If an error occurs then the err output will be a negative error code. Otherwise the err output will be zero.
The connection is closed when the model is terminated or the cls input is non-zero. Note that the cls input must be maintained at a non-zero value to ensure that the connection remains closed. Otherwise the Mavlink Initialize block will reconnect.
Communication channels are identified by a Universal Resource Identifier (URI), such as udp://localhost:14550?peer=manual, tcpip://remotehost:5760 or serial://localhost:1?baud=115200. QUARC uses URI's for all its communications because it provides a uniform, extensible and flexible means of identifying the communication protocol to use and the associated communication parameters. Refer to Universal Resource Identifiers for more information.
 When using the UDP protocol as a server, the
When using the UDP protocol as a server, the peer=manual option should be specified on the URI e.g. udp://localhost:14550?peer=manual
so that the Mavlink Initialize block can communicate with multiple drones at the same time. This option allows the Mavlink Initialize block to track the IP address
of each drone and direct messages to/from specific drones simultaneously.
The URI may be specified in the dialog parameters or via an input port. Which option is used is determined by the Source of URI parameter. When the URI is specified via an input, the input is typically driven by a Model Argument block, which allows a model argument to be used to assign the URI at runtime.
 When the URI is specified as a dialog parameter and is not evaluated then the URI is configuration-dependent.
A separate URI may be entered for each model configuration as well as for normal simulation.
Thus, it is possible to employ a different URI for each target, without making a new diagram. The
URI that is entered becomes the URI for the currently active configuration when the Simulation mode
is set to . It becomes the URI for normal simulation when the Simulation
mode is set to .
When the URI is specified as a dialog parameter and is not evaluated then the URI is configuration-dependent.
A separate URI may be entered for each model configuration as well as for normal simulation.
Thus, it is possible to employ a different URI for each target, without making a new diagram. The
URI that is entered becomes the URI for the currently active configuration when the Simulation mode
is set to . It becomes the URI for normal simulation when the Simulation
mode is set to .
Streams have an associated buffer that is independent of any buffering in the underlying protocol. The stream buffer is designed to maximize use of the available bandwidth. For example, it only reads from the underlying communication channel when there is not enough data in the stream buffer, at which point it attempts to read enough bytes to fill the entire stream buffer.
Helpful Hints
UDP Options
 When using the UDP protocol as a server, the
When using the UDP protocol as a server, the peer=manual option should be specified e.g. udp://localhost:14550?peer=manual.
This option allows the Mavlink Initialize block to communicate with multiple drones simultaneously.
Multiple NICs and UDP
 When using the UDP protocol, the network interface card (NIC) from which datagrams are received may be specified using the
nic option. Refer to the UDP Protocol for details.
When using the UDP protocol, the network interface card (NIC) from which datagrams are received may be specified using the
nic option. Refer to the UDP Protocol for details.
Input Ports
cls
Used to close the connection. Setting this input to a non-zero value will cause the connection to be closed. The connection will remain closed
as long as this input is non-zero. When this input is zero or false, then a new connection will be established. The connection will be maintained as
long as this input is zero.
uri
A string specifying the URI to which to connect or upon which to listen for client connections. The string must be a null-terminated
vector of characters represented as a vector of uint8 quantities. It may be variable-sized. This string is typically provided
either directly or indirectly by a Model Argument
block or String Constant block.
This input is only available if the Source of URI parameter is
set to External input port. Refer to the documentation below on the
Source of URI parameter for details.
Output Ports
con
A uint8 state code indicating the current status of the connection. The different connection states and their values are given in the table above in the Description section.
err
An int32 error code indicating the results of the operation. If there are no errors during the establishment of a connection, then
this output will be zero. The -QERR_WOULD_BLOCK error is never output at this port, even though non-blocking I/O is used, because this
condition is not considered an error by the block. Otherwise another negative error code is returned. See
Error Codes for the different error codes and their values. Use the
Compare to Error block rather than the error code itself to check for specific error codes.
Parameters and Dialog Box
Go to Mavlink blocks using this connection
Opens a dialog that lists all the Mavlink blocks in the model which are currently using the same connection selected in the Connection name parameter. The dialog may be used to go to another Mavlink block in the model just by double-clicking on the name of the block in the dialog box.
Individual Panes
The parameters of the Mavlink Initialize block are divided into three categories: Main, Messages and Outputs.
The Main tab contains the parameters used frequently, such as various communications parameters and the sample time.
The Messages tab is used to define the Mavlink messages supported by the block. The block is able to read a Mavlink message definition file and automatically support the messages defined in that file. Thus, even custom messages are supported, provided they are defined in the message definition file. Message definition files may include other message definition files.
Finally, the Outputs tab specifies the values to write to the motors when the model is stopped.
Use the links below to jump to the documentation for each tab:
Main Pane
The Main pane of the dialog appears as follows:
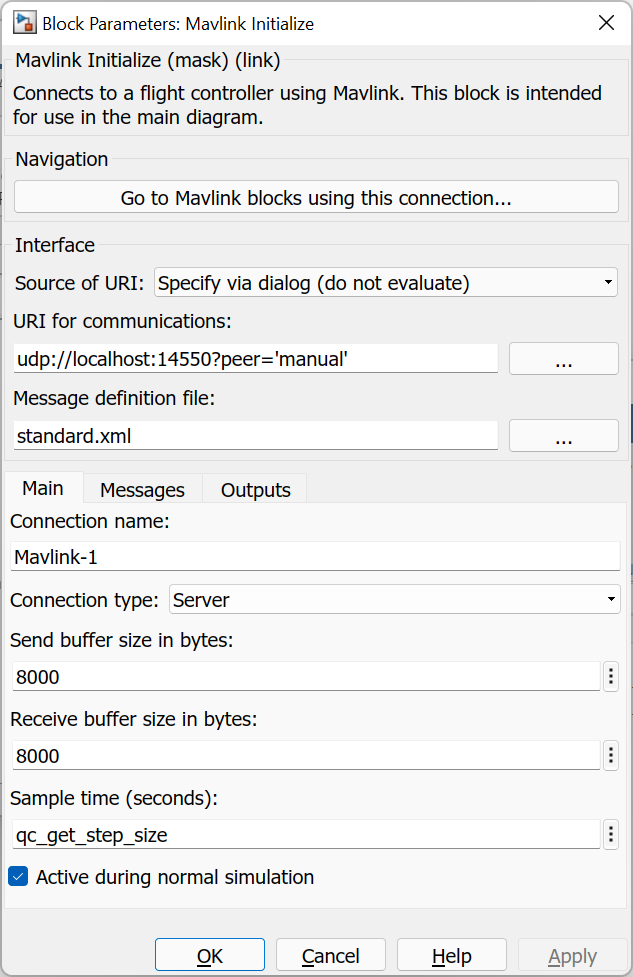
Connection name
The name to assign to the connection. This name will show up in the list of connections for the other Mavlink blocks. It is this name that associates the other Mavlink blocks with the Mavlink communication channel selected by this block.
Connection type
Whether to establish a client or a server connection to the drone(s). Client connections only support a single drone. Server connections support multiple drones if the UDP protocol is used.
Source of URI
Indicates whether the URI should be determined from the dialog parameters or an
input port. If this field is set to Specify via dialog (do not evaluate) then
the URI is specified via the URI for communications
parameter. In this case, the URI is not evaluated as a MATLAB expression but is
interpreted as a literal string. However, format specifiers are recognized. Refer
to qc_perform_substitutions
for a list of the format specifiers available.
 If format specifiers which change frequently, such as '%{time}' or
'%{instance}', are used in the URI then the Mavlink Initialize block cannot be placed
in a referenced model, because the URI will change from the time the code is built to when
the code is run. As a result, Simulink will insist that the code be rebuilt because block
parameters in referenced models are inlined. Instead, specify the source of the URI as
If format specifiers which change frequently, such as '%{time}' or
'%{instance}', are used in the URI then the Mavlink Initialize block cannot be placed
in a referenced model, because the URI will change from the time the code is built to when
the code is run. As a result, Simulink will insist that the code be rebuilt because block
parameters in referenced models are inlined. Instead, specify the source of the URI as
External input port and pass the URI from the top-level model. Use a
String Constant block
in the top-level model to generate the URI.
If this field is set to Specify via dialog (evaluate) then the URI is also specified
via the URI for communications parameter. However, in this case,
the URI is evaluated as a MATLAB expression. This option is convenient for using a variable
in the MATLAB workspace for the URI.
If this field is set to External input port then the URI for communications
parameter is ignored and an extra input port is provided which determines the URI.
URI for communications (tunable offline)
The URI identifying the communication channel to which to connect or upon which to listen for connections from drones, and the
associated communication parameters. For example, udp://localhost:14550?peer=manual listens for
connections on UDP port 14550 and allows the Mavlink Initialize block to communicate with multiple drones simultaneously.
This field is only used if the Source of URI parameter is set to Specify via dialog (do not evaluate)
or Specify via dialog (evaluate). Refer to
Universal Resource Identifiers for more information about URIs
and the communications protocols supported by QUARC.
Send buffer size in bytes (tunable offline)
The size of the buffer used by the stream for sending data. This buffer is independent of any buffering in the underlying communication protocol. Increasing the buffer size may increase transmission performance. The buffer size must be at least as large as the maximum vector that will be sent. For example, if a double 3-vector is transmitted using the Stream Write block then the stream buffer size must be at least 24 bytes in length since a double is 8 bytes and a 3-vector is being sent.
Receive buffer size in bytes (tunable offline)
The size of the buffer used by the stream for receiving data. This buffer is independent of any buffering in the underlying communication protocol. Increasing the buffer size may increase reception performance. The buffer size must be at least as large as the maximum vector that will be received. For example, if a double 5-vector is received using the Stream Read block then the stream buffer size must be at least 40 bytes in length since a double is 8 bytes and a 5-vector is being received.
Sample time
The sample time of the block. A sample time of 0 indicates that the block will be treated as a continuous time block. A positive sample time indicates that the block is a discrete time block with the given sample time.
A sample time of -1 indicates that the block inherits its sample time. Since this is a source block, only inherent the sample time when it is placed in a conditionally executed subsystem, like a Triggered Subsystem, Enabled Subsystem, Function Call Subsystem or in a referenced model.
To use the fundamental sampling time of the model, set the sample time to qc_get_step_size, which is a QUARC function that returns the fundamental sampling time of the model.
The default sample time is set to qc_get_step_size.
Active during normal simulation (tunable offline)
Indicates whether this block should execute during normal simulation. If this option is not checked then the block will not listen for or accept connections during normal simulation. This parameter has no effect on generated code.
Messages Pane
The Messages pane of the dialog appears as follows:
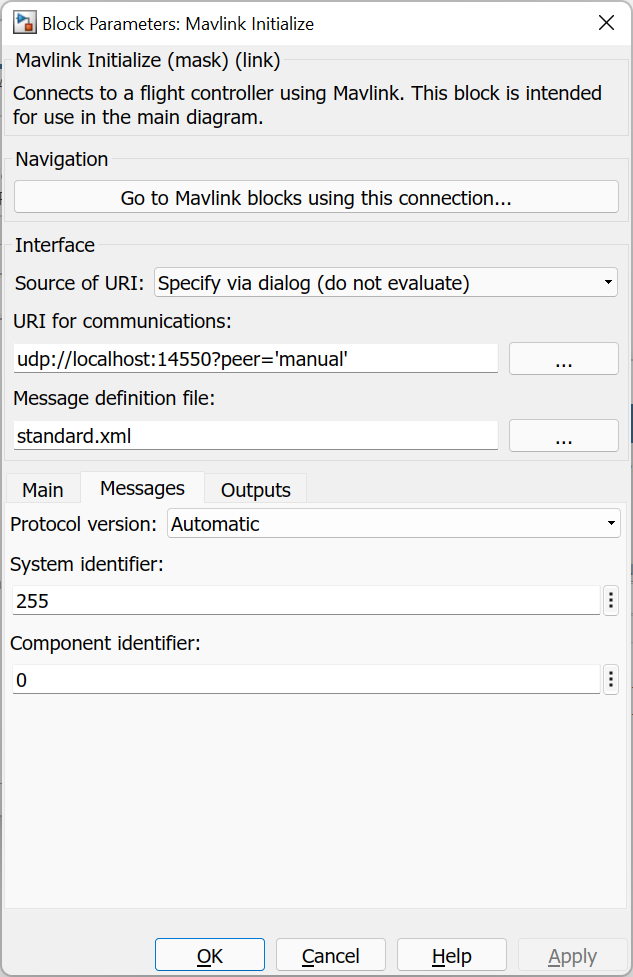
Message definition file
Specifies the message definition file defining the messages to use for messages sent and received using this connection.
System identifier
The identifier of the Mavlink system represented by this block.
Component identifier
The identifier of the Mavlink component represented by this block.
Outputs Pane
The Outputs pane of the dialog appears as follows:
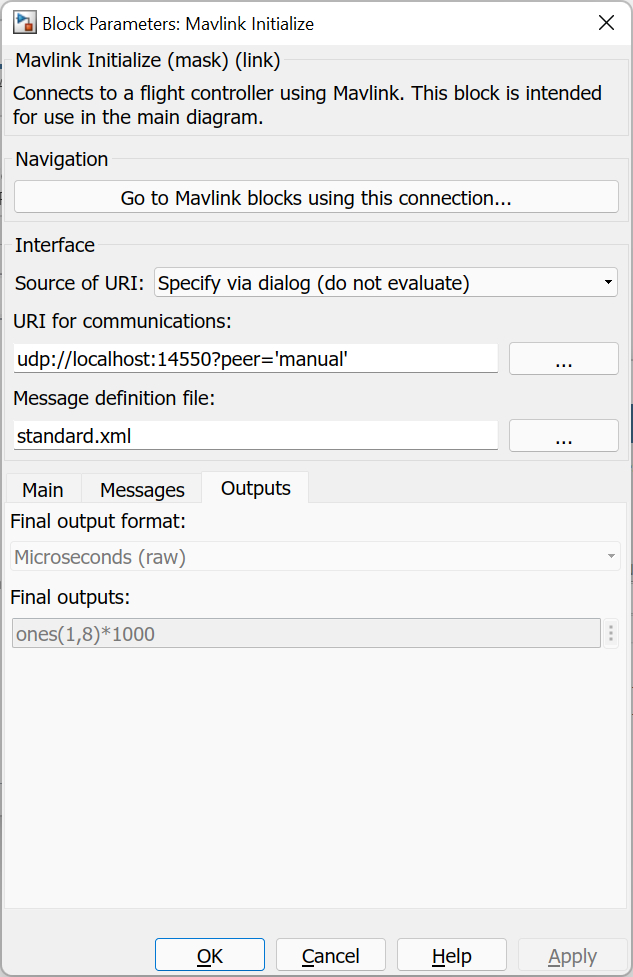
Final output units (tunable offline)
The units to use for the Final outputs parameter. The table below shows the input for each of the different units:
|
Units |
Data Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Bipolar percentage |
double |
Each element maps the input range of [-1,1] to the typical [1000,2000] range such that -1 becomes 1000, 0 becomes 1500 and 1 becomes 2000. Any values outside this range are mapped according to the same affine transformation. These units are useful when the RC data represent -100% to 100% throttle. |
|
Unipolar percentage |
double |
Each element maps the input range of [0,1] to the typical [1000,2000] range such that 0 becomes 1000 and 1 becomes 2000. Any values outside this range are mapped according to the same affine transformation. These units are useful when the RC data represent 0 to 100% throttle. |
|
Seconds |
double |
Each element maps the input range of [0.001,0.002] to the typical [1000,2000] range such that 0.001 becomes 1000 and 0.002 becomes 2000 so that the input is the RC pulse width in seconds. Any values outside this range are mapped according to the same affine transformation. These units are useful when the RC data are being used to drive PWM pulse widths via the HIL blocks. |
|
Microseconds (raw) |
uint16 |
Each element is the raw RC value, which is the RC pulse width in microseconds. |
Final outputs (tunable online)
The final output values to write to the motors when the model is stopped. The Mavlink Initialize block ensures that these values are written to the actuators on model termination so that the motors do not continue spinning. If this parameter is an empty matrix then no final outputs are written.
Targets
|
Target Name |
Compatible* |
Model Referencing |
Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
||
|
Yes |
Yes |
Last fully supported in QUARC 2018. |
|
|
Rapid Simulation (RSIM) Target |
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
S-Function Target |
No |
N/A |
Old technology. Use model referencing instead. |
|
Normal simulation |
Yes |
Yes |
See Also

Copyright ©2025 Quanser Inc. This page was generated 2025-11-01. Submit feedback to Quanser about this page.
Link to this page.