

RCP CL HIL Read Timebase Example
This example is a simple analog loopback test where The CL HIL Read Timebase VI synchronizes the loop to the hardware timebase. It demonstrates a number of important features of RCP, such as the ability to access and quickly change hardware, online parameter tuning, data streaming, and potentially more. For a detailed description of these VIs and how they operate, please refer to the RCP HIL Initialize, CL HIL Read Timebase and CL HIL Write help pages.
System Requirements
Please refer to the Rapid Control Prototyping (RCP) Toolkit System Requirements to run this example. This example requires data acquisition hardware with at least one set of Analog I/O channels supported by the HIL Initialize VI, such as the Quanser Q2-USB hardware-in-the-loop card. Refer to the RCP Data Acquisition Card Support page for a full list of the RCP-supported HIL boards. This example also requires an RCA loopback cable.
Configuring the Example
Open the RCP CL HIL Read Timebase Example.vi under My Computer in the LabVIEW project.
To set up the example for a RCP-supported data acquisition card, select Show Block Diagram from the Window menu or press Ctrl+E
while the Front Panel is the active window. Double click the HIL Initialize VI and select the correct board type from the
Board type combo box. If you have more than one board of the same type in your computer, change the Board Identifier field to
the board you wish to use. Boards are numbered from 0 such that board 0 is the first board recognized by the HIL Initialize VI. Press
the to apply the changes and close the Configure HIL Initialize window.
Close the Block Diagram window after all changes to
the system have been made.
For example, for the Q2-USB hardware-in-for-loop card, simply connect an RCA cable from Analog Output #0 to Analog Input #0 on the terminal board.
Running the Example
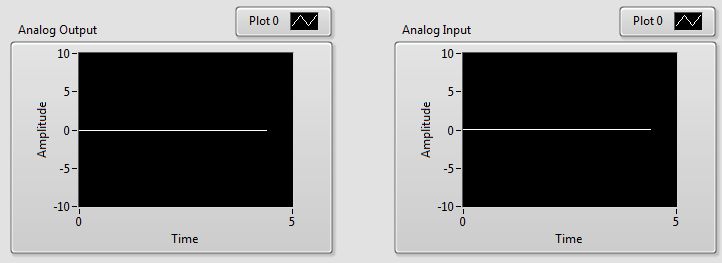
Click on the VI button or select from the menu to start the VI. A straight line with an amplitude of 0 will
appear in the Analog Input and Analog Output graphs. Notice that the graph trace
is now moving in real-time. In other words, the trace passes the 5-second mark after 5 seconds have passed.
Click on the orange circle on the Knob labeled Analog Output Signal and move the dial until the output
value is 5 V. The Analog Output graph displays the value of the Analog Output Signal
and the Analog Input displays the value measured from the Analog Input channel #0
from the PC data acquisition card.
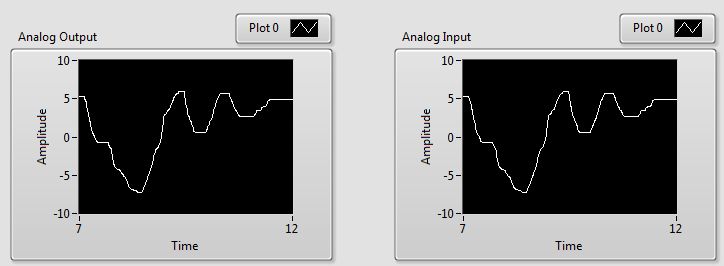
The Analog Input graph should display the same signal as the
Analog Output graph because the input channel is connected to the output channel via the RCA cable.
If the Analog Input graph does not change as the Analog Output Signal dial is rotated
verify that the RCA cable from analog output #0 is properly connected to analog input #0 on the
corresponding RCA connectors and the HIL Initialize VI has the correct board type selected.
Click on the Front Panel button to stop the VI.

Copyright © Quanser Inc. This page was generated 2021-09-24. Submit feedback to Quanser about this page.
Link to this page.